Abstract
As we all know about the current pandemic spread due to the novel coronavirus, known as the novel coronavirus disease – 2019 (CoVID-19; WHO, 2019). People are also experiencing psychosocial problems amid this pandemic. People who are using tobacco products in various forms may be at a greater risk of getting CoVID-19 positive very easily. Smoking causes chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases which is the fourth leading cause of death and one of the primary risk factors for CoVID-19. Although there is no specific vaccine for treating novel coronavirus diseases, still there may be some preventive and adaptive strategies to save oneself from getting the infection, to save oneself from the psychosocial crisis caused due to lockdown and self-quarantine, and to save oneself from using tobacco. The paper described coronavirus diseases, its impact on psychosocial life, relationship with tobacco use, and possible preventive and adaptive strategies.
Full-length article
Pandemic is usually spread due to novel diseases that have no treatment at the time of emergence. The spread of the new disease without any cure costs the lives of many people and termed as epidemic. Other diseases have also been evident in human history for different kinds of pandemics. These may include measles, swine flu, Ebola virus, malaria, Spanish flu, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), or Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome (SADS). Some of the viruses enter into the human community from animals. For example, SARS-CoV transmitted from civet cats and this led to an epidemic that occurred in 2003 in china. Similarly, MERS transmitted from camels in the middle east (Saudi Arabia) in 2012, and SADS transmitted from swine to human population first in China in the year 2017.
All of these epidemic diseases were controlled and managed through the development of new vaccine treatment. There has been a new virus that led to another pandemic worldwide. This was known as novel coronavirus disease and the World Health Organization termed it as CoVID-19 in December last year. There are generally four categories of different coronaviruses – alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. The novel coronavirus disease assumed to be beta coronavirus that might probably be transmitted into humans from bats. However, the CoVID-19 like previous diseases such as SARS-CoV and SADS was first reported from a wet animal market of Wuhan province in China,in December last year. It was reported that the novel coronavirus was spread from seafood sellers and animal marketers to other people such as their family members, relatives, and associated health workers. It was first assumed to be a pneumonic disease having respiratory symptoms like dry cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Gradually it was spread to other countries as well, and led to the worst pandemic of the time leading to global death toll to more than 1.5 lakh till April 19, 2020.
Still, no specific vaccine has been found.They are currently under development. To the date, the worst-hit countries are the United States, Italy, Spain, France, China, and the United Kingdom (U.K.) till April 19, 2020 (Worldometers.info, April 20, 2020). The epidemic of CoVID-19 is observed to be as more dangerous than the previous types of coronavirus diseases discussed above because the novel coronavirus is a linear single-stranded positive-strand RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) genome of about 30 kb that is mutable. It means it may directly impact the genetic material present in human cells. The virus can only be weakened through the body’s immune cells. People having less immunity are more vulnerable to have a severe condition of CoVID-19. This disease spread through contact such as touching objects and being in close to someone else. The pandemic has been proved as causing a number of psychological problems as well such as anxiety. People having CoVID-19 test as positive are at a greater risk of getting depression. They may feel a heightened grief, sadness, loss of family contact, loss of contact with friends and other support people, loss of trust in God and religious activities, or an experience of death anxiety if the case is most severe.
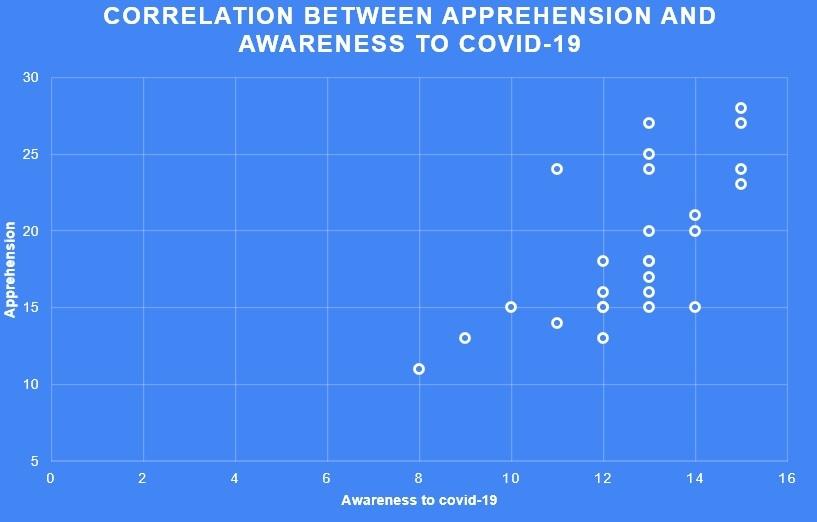
People may also be anxious if they have the real awareness of the coronavirus and its impacts. A small survey was conducted to see the relationship between apprehension and awareness of coronavirus. Two self-made questionnaires were used to collect the data for apprehension and awareness of CoVID-19. A total of 26 participants took both the questionnaires. Concerning the awareness questionnaire,scores were calculated based on the right and wrong answers whereas concerning the apprehension questionnaire scores were calculated based on the Likert scale. The correlations coefficient between the awareness to CoVID-19 and apprehension was found to be +0.66 which is a good correlation (figure 1.1).
Scatter plot
It means people who have a real awareness of this pandemic, also experience apprehension which is the primary characteristic of anxiety. Generally, people are more anxious when they have less information about the real impact of any disease. For example, for cancer diseases, most of the people show anxiety and sadness because it is directly linked to death. Similarly, in this survey study, it was found that people who were more conscious of the current pandemic disease such as its symptoms, impacts, or treatment were also experiencing some kinds of apprehension. However, these are the psychological impacts of coronavirus (figure 1.2).
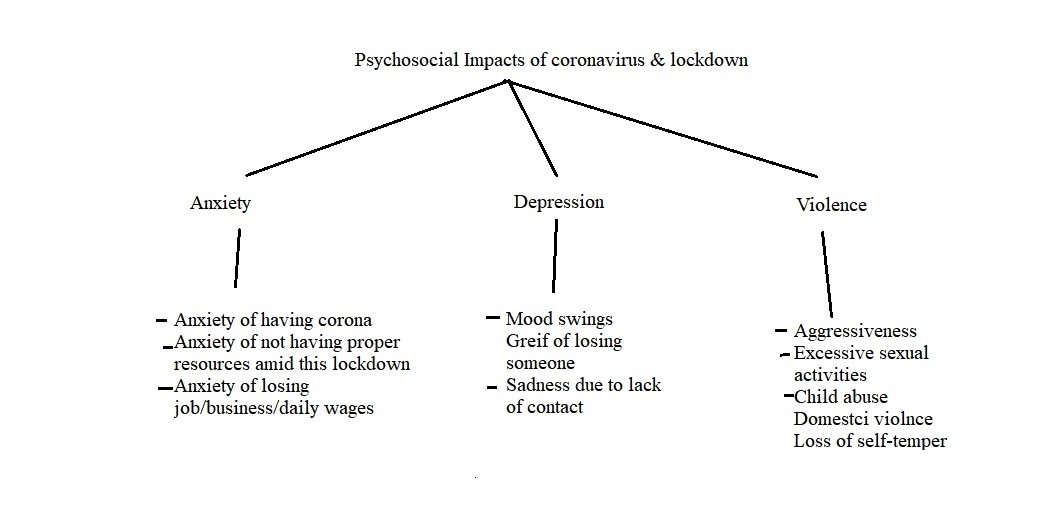
Psychosocial impacts of coronavirus
There is also the other side of this outbreak of novel coronavirus pandemic.It is the negative impact of quarantine and lockdown on peoples’ psychosocial life. Due to this, people are not able to live their social life as usually they used to live. They fear of being corona positive that’s why they prefer to remain at home under self or institutional quarantine. However, living in the quarantine for a longer period brings boredom, mood swings, emotional instability, and cravings for different basic needs – such as craving for food, sex, substance use, and affiliation. People who feel boredom and experience intense cravings for their basic needs to be fulfilled are at a greater risk of having emotional and physical outbursts that may result in increased aggressiveness, domestic violence, child abuse, or sexual abuse. The Guardian has reported increased cases of domestic violence in their report that is caused due to lockdown and quarantine (The Guardian, March 28, 2020). It is very difficult for abusers to control their aggressive impulses under the longer period of quarantine and complete lockdown of in city or state. People who are addicted to tobacco and alcohol may find it very difficult to arrange the substance amid this lockdown that further create intense cravings and severe withdrawal symptoms. Ultimately, the result is the loss of self-temper and increase chances of domestic or physical violence. Therefore, it has been reported from various places that some people are facing difficulty in living with their partner due to a long period of quarantine.
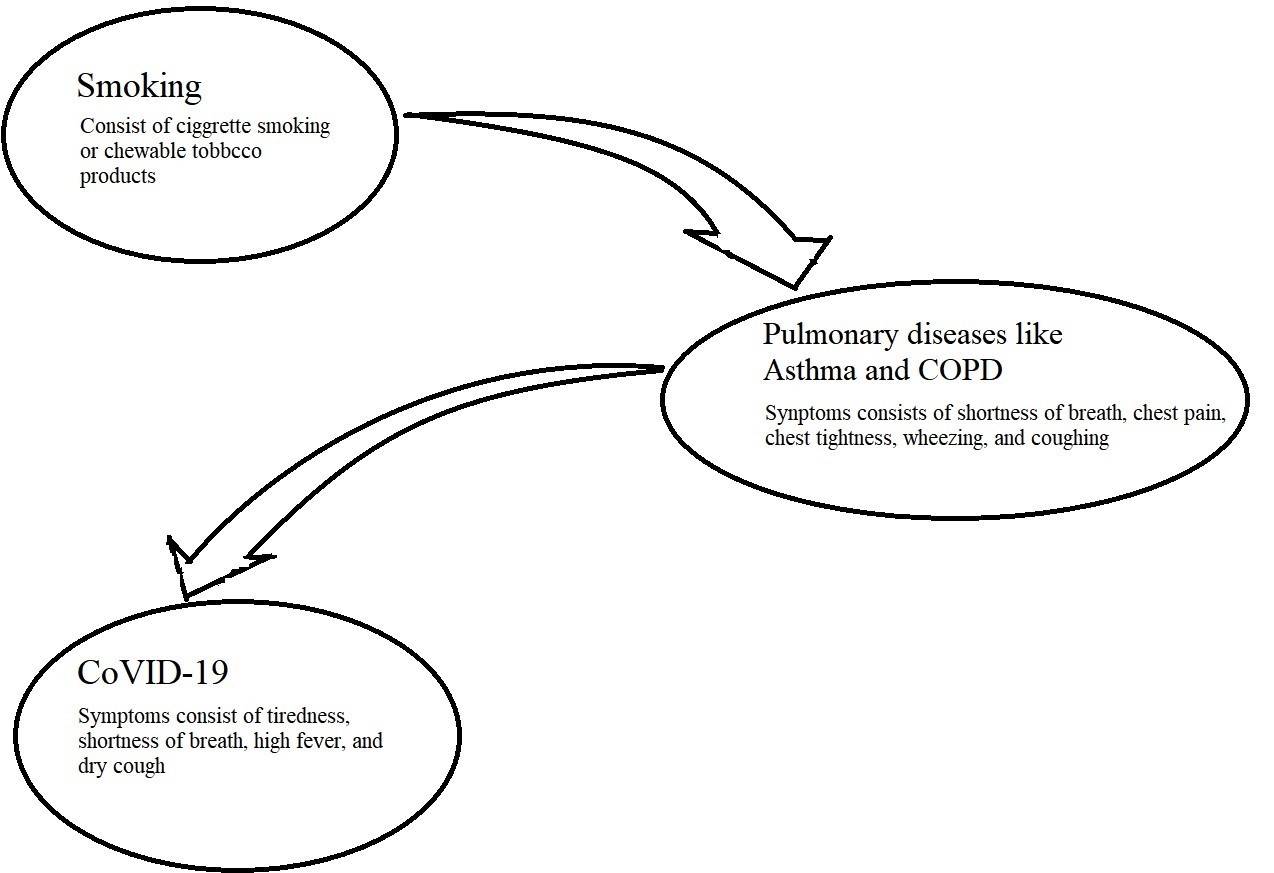
The primary risk factor of CoVID-19 is close contact with the infected person or coming in contact with the surface, place, or any object which is already infected. There is another risk factor which is the use of tobacco products like cigarettes(or bidi) smoking and chewable tobacco products. Cigarettes, bidi, electronic-cigarettes(currently illegal in India), and cigar are smoked tobacco products. Whereas, betel quid(gutkha), khaini (tobacco with slaked lime), panmasala (a mixture of areca nut, catechu, tobacco and other flavors), or dry tobacco are chewable tobacco products. All these products contain tobacco which is the most dangerous substance for pulmonary functioning. It consists of approximately 7,000 chemicals, the most dangerous chemicals are butane, nicotine, cadmium, arsenic, aldehyde, ammonia, methanol, carbon monoxide, and others. Nicotine is the only chemical that has addictive properties and makes a person dependent on the tobacco or cigarette smoking. Out of these 7,000 chemicals, 69 are called carcinogens which causes cancer diseases such as lung cancer. Cigarette smoking is the primary risk factor for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). According to WHO, COPD is the third leading cause of death worldwide (WHO, 2016). It has been found that CoVID-19 has four primary symptoms – tiredness, shortness of breath, dry cough, and high fever, out of these, shortness of breath and dry cough are directly linked to lungs. Any kind of preexisting pulmonary disease like COPD and asthma increases the severity of already diagnosed coronavirus disease, which may even lead to death (figure 1.3).
Older people are also at a greater risk because they have a weak immune system that leads to lower production of immune cells to fight with the coronavirus in the body. On the other hand, people who have been diagnosed with CoVID-19 and already have a history of tobacco use, are at a greater risk of getting their condition more severe (WHO, 2020). Autopsy studies on dead corona patients and CT scan have revealed that novel coronavirus is leaving a different kind of patches along the outer sides of the lungs (Zhang, Y., et. al., 2020). These patches are quite similar to the patches found in the lungs of people who use tobacco products (The Telegraph, February 14, 2020).
It is very much clear that CoVID-19 is dangerous for human life because it has no specific vaccine while it may be more dangerous for the people who have corona symptoms or who have been diagnosed with it and who are using tobacco products. But still there is a hope to avoid the spread of this disease and to minimize the risk factors such as tobacco use. Some possible prevention and solutions are discussed below that may be adopted to avoid the spread of coronavirus as well as to reduce the chance of getting coronavirus positive by quitting tobacco consumption.
Preventing strategies to stop the spread of coronavirus:
- CoVID-19 is a disease that has no known origin, exact causes, and specific vaccine. So, the only option is to maintain social distance from everything including people and objects. Maintain at least six feet distance from people and objects near you.
- Wash your hands properly and frequently as suggested by WHO and health ministry.
- Keep yourself updated with minerals, necessary nutrition like food and fruits, and do regular indoor exercises. It will increase your stamina and immunity that is good to fight with coronavirus if you get infected.
- If you have these symptoms – dry cough, shortness of breath, tiredness, and high fever, usually more than 102-degree Fahrenheit, then contact health professional in your district hospital or call at coronavirus helpline numbers. For example, use a central helpline number +91-11-23978046.
- Hands may be contaminated because we touch a lot of things in our everyday life that may have coronavirus, therefore avoid touching your nose, eyes, and face. The virus from hands may enter into your body through nose, eyes, and mouth.
- Maintain a strict social distance of at least six feet between you and other people.
- If you get to know about anyone who has symptoms of CoVID-19 or have been diagnosed with it, then be cautious and avoid physically contacting him/her further.
- Be careful of your health, take proper night sleep, bath from fresh water daily, and clean your home and other stuff regularly.
Adapting strategies to overcome psychosocial problems caused due to lockdown or self-quarantine:
- Be connected with people through digital platforms, however, be also cautious of online frauds and never share your private information on any web-portal.
- Be connected with people over telephone, chats, video calls, and other social sites.
- Consider the time of quarantine as holidays and enjoys with your family, spouse, or children.
- Try to cook and eat together within your family and engage family talk and listening. It will maintain a healthy emotional life and family attachments.
- Try to avoid the regular news update related to fatalities due to CoVID-19. Think positive and do your work from home.
- Be busy with games and other important works.
- Try to ignore family members from whom you get annoyed or angry over petty issues. It will help you to remain away from aggressive behaviors and possible occurrence of domestic violence.
- Perform prayers at home and be engaged in any kind of relaxation exercise like meditation for at least five minutes daily.
- Support each one through understating, sympathizing, and listening. It will help you to maintain a healthy bond within the family and with friends or neighbors.
- If you find any difficulty in concentrating, feel fatigues, overburdened, slow, sad, or bored then contact a person closed to you. That person may be your spouse, best friend, or relatives. If the problem continues and nothing happens good to you then seek professional help such as contacting a counselor. For domestic violence cases, you may reach the national commission of women helpline numbers 011-26942369, 26944754, and for child abuse, you may reach at student/child helpline 1098.
Preventive and adaptive strategies to successfully quit tobacco use.
- Try to reduce your daily number of cigarettes or other products gradually in decreasing order. For example, if you take 5 per day then take 4 the next day, and continue to decrease the numbers till 0 comes.
- When quitting tobacco, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as headache, head throbbing, chest tightness, irritation, clumsiness, nausea, nervousness, sweating, or heart palpitations. These are not the disease or disorder and you do not need to worry. These symptoms remain for a very brief time usually from 5 to 10 minutes. You can control these cravings by following these things:
- Take a glass of water with lemon juice and one spoon of honey and drink it. It will help you to calm down the physical cravings caused due to tobacco withdrawal.
- Eat citric fruits such as orange, pineapple, and grapes because citric fruits consist of citric acid that acts as a detoxifying agent to remove the chemical of tobacco from the body. Removal of tobacco chemicals from the body decreases the physiological cravings.
- Avoid contacting your friends and family members when they use tobacco products. Avoid objects and specific places that may trigger cravings for tobacco/cigarette use. For example, it may be a coffee cup if you take coffee along with the cigarette or it may be a terrace if you usually smoke at the terrace of your house.
- Keep a mixture of these things – anise (saunf), cardamom(elaichi), sugar chunks (mishri), dry ginger (sookhaadrak), and dry gooseberry (sookhaaanwla). Grind these things coarsely and chew instead of chewing tobacco (like gutkha or khaini) or smoking a cigarette. It will help to maintain freshness in the mouth and will take away the bad smell of tobacco from the mouth.
- Whenever you feel intense cravings, divert your mind through watching a favorite movie, playinga game, talking to best friends over the phone,being with your loved one, or reading an interesting book, magazine, or comic.
- If these steps are unhelpful for you to quit tobacco then you should seek further support from a counselor or health professional providing the tobacco counseling. You may call to national helpline number of tobacco quit line service at 1800-11-2356.
References:
Banschick, M. (2020, March 12). The Social Consequences of Coronavirus. Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/the-intelligent-divorce/202003/the-social-consequences-coronavirus
Bhargava, H. D. (2020, April 17). Coronavirus: What Happens to People's Body If They Get Infected. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/lung/coronavirus-covid-19-affects-body#1
Chadda, R. K., & Sengupta, S. N. (2002). Tobacco use by Indian adolescents. Tobacco Induced Diseases, 1(1), 8.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US). (1970, January 1). Cancer. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53010/
COPD. (2020, April 15). Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/copd/symptoms-causes/syc-20353679
Coronavirus Cases (April 20, 2020). Retrieved from https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
Eastern Mediterranean Region. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.emro.who.int/tfi/know-the-truth/tobacco-and-waterpipe-users-are-at-increased-risk-of-covid-19-infection.html
Fan, Y., Zhao, K., Shi, Z. L., & Zhou, P. (2019). Bat Coronaviruses in China. Viruses, 11(3), 210.
Gulland, A. (2020, February 14). Smokers at increased risk of coronavirus complications, leading experts warn. Retrieved from https://www.telegraph.co.uk/global-health/science-and-disease/coronavirus-dangerous-smokers/
Graham-Harrison, E., et. al. (2020, March 28). Lockdowns around the world bring rise in domestic violence. Retrieved from https://www.theguardian.com/society/2020/mar/28/lockdowns-world-rise-domestic-violence
Li, C., Yang, Y., & Ren, L. (2020). Genetic evolution analysis of 2019 novel coronavirus and coronavirus from other species. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 104285.
The top 10 causes of death. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death
Like!! Really appreciate you sharing this blog post.Really thank you! Keep writing.
You are most welcome 🙂